The rapid evolution of modern electronics has led to the increasing adoption of advanced circuit board technologies, among which the rigid flex PCB stands out as a game-changer. Combining the advantages of both rigid and flexible printed circuit boards, rigid flex PCBs provide unparalleled design flexibility and space savings for a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to aerospace devices. As technology becomes more compact and intricate, the demand for reliable and efficient interconnect solutions has soared, making rigid flex PCBs an essential component in the design of innovative electronic products.
In this ultimate guide, we will explore the myriad applications and benefits of rigid flex PCBs, highlighting how they enhance the performance and reliability of modern electronics. By integrating the best features of rigid and flexible circuits, these hybrid solutions offer significant advantages, such as reduced weight, increased durability, and improved thermal management. As industries continue to push the boundaries of technology, understanding the potential of rigid flex PCBs becomes crucial for manufacturers and engineers aiming to stay ahead of the curve. Join us as we delve into the transformative impact of rigid flex PCBs on contemporary electronic systems, paving the way for more efficient, compact, and innovative designs.
Rigid Flex PCBs, or printed circuit boards, combine the best features of both rigid and flexible circuits. These boards are designed to withstand the mechanical stresses typical in modern electronic devices while offering the adaptability needed for complex layouts. The structure of a rigid flex PCB consists of multiple layers, including rigid sections made from traditional materials like FR-4 and flexible materials such as polyimide. This unique combination allows for intricate designs that can bend and fit into compact spaces without compromising functionality.
The definition and structure of rigid flex PCBs highlight their versatility in various applications. In essence, they enable manufacturers to create lightweight and space-efficient products while enhancing reliability. The layers of the PCB are bonded together, allowing the rigid segments to provide structural support, while the flexible parts facilitate movement and flexibility. This makes them ideal for applications ranging from consumer electronics and medical devices to aerospace and automotive industries, where performance and design flexibility are paramount.
Rigid flex PCBs have become increasingly popular in modern electronics due to their versatility and ability to save space. One of the key applications is in smartphones and wearable devices, where the demand for compact designs is paramount. Rigid flex circuits allow for intricate designs that combine both rigid and flexible elements, enabling manufacturers to create slimmer profiles while ensuring durability. This is particularly important in mobile devices, where size constraints and operational stress require reliable connections without compromising performance.
Another significant application of rigid flex PCBs is in medical devices. The growing trend towards miniaturization in healthcare technology has prompted the need for advanced packaging solutions. Rigid flex circuits offer the reliability needed in critical medical applications, such as telemetry devices and portable diagnostic equipment. Their unique construction facilitates complex routing over multiple layers, supporting the integration of various functions within a constrained space. This not only enhances device performance but also improves patient comfort, as smaller and lighter devices are easier to manage in medical settings.
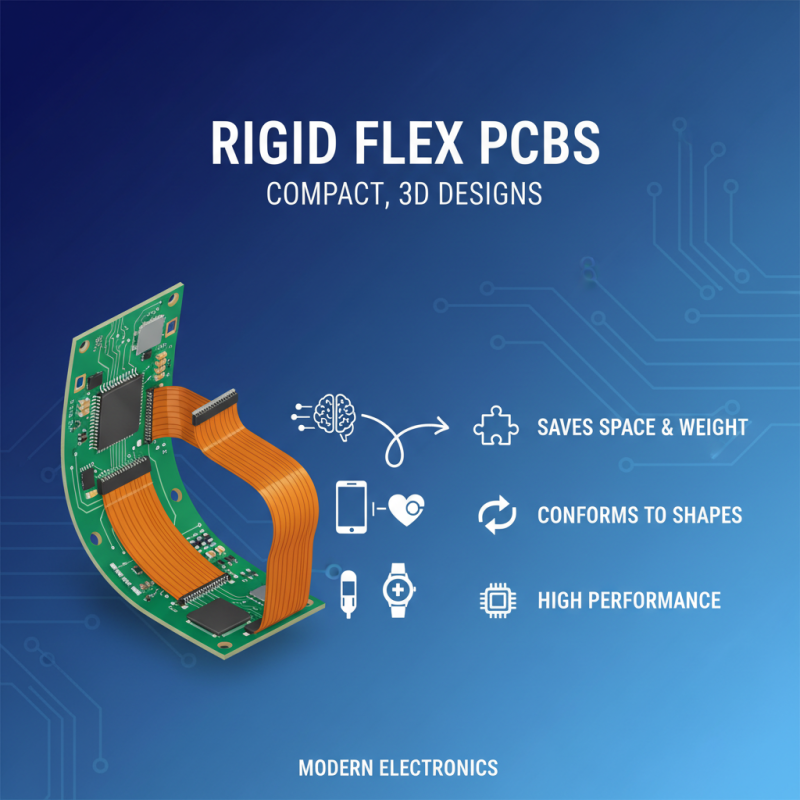
Rigid flex PCBs combine the benefits of both rigid and flexible circuits, making them an ideal choice for modern electronics that demand high performance and compact designs. One of the primary advantages of rigid flex PCBs over traditional PCB designs is their ability to conform to complex 3D shapes. This flexibility allows for innovative product designs that can fit into tighter spaces, reducing the overall footprint of the device. In applications such as wearables, smartphones, and medical devices, where efficient use of space is critical, rigid flex PCBs provide a significant edge by enabling designers to integrate components in a more streamlined manner.
Another key benefit of rigid flex PCB technology is improved reliability. Traditional PCBs often require multiple interconnects, which can lead to increased points of failure. In contrast, rigid flex designs minimize the number of interconnections by combining rigid and flexible substrates into a single unit, thus enhancing durability and longevity. This reduction in mechanical stress and potential breakage makes rigid flex PCBs particularly suited for applications exposed to dynamic environments, such as automotive and aerospace industries. Additionally, the capability to withstand thermal expansion and contraction without compromising performance further establishes rigid flex technology as a superior choice in many high-tech applications.
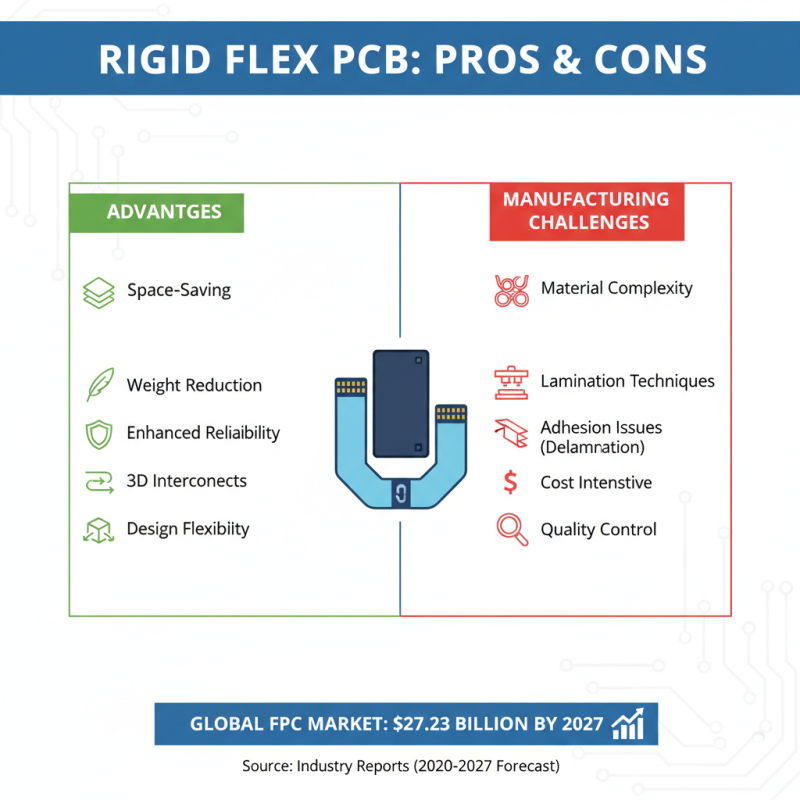
Rigid Flex PCBs offer numerous advantages for modern electronics, but their manufacturing process presents unique challenges. One major consideration is the complexity of the materials involved. Rigid Flex PCBs combine flexible and rigid substrates, often requiring specific laminating techniques and adhesives. Reports indicate that the global flexible printed circuit board market is expected to reach USD 27.23 billion by 2027, emphasizing the increasing adoption of such technologies and the need for high-quality manufacturing standards. The integration of advanced materials can lead to issues like delamination and poor adhesion if not handled properly.
Moreover, managing the thermal and mechanical stresses during the production of Rigid Flex PCBs poses another challenge. These boards must endure various environmental conditions, making it crucial to select materials that not only withstand these factors but also maintain electrical reliability. Industry studies suggest that approximately 25% of PCB failures stem from material selection and processing techniques, underscoring the importance of meticulous design and production processes.
**Tips**: When considering Rigid Flex PCB manufacturing, invest time in selecting compatible materials and conduct thorough testing to ensure performance reliability. Collaborating with specialists during the design phase can mitigate potential issues before production begins. Always keep abreast of the latest advancements in PCB technology to enhance the overall manufacturing process and product quality.
As technology advances, the applications of rigid flex PCBs are becoming increasingly prevalent across various sectors, particularly in modern electronics. One of the key future trends is the miniaturization of devices, which demands smaller and lighter components. Rigid flex PCBs offer a unique solution as they combine the properties of both rigid and flexible circuits, enabling designers to create compact and intricate layouts that can fit into limited spaces while maintaining functionality and reliability. This trend is particularly relevant in industries such as medical devices, wearables, and consumer electronics, where the demand for portability and performance continues to grow.
Another significant trend is the rising integration of IoT (Internet of Things) technologies with rigid flex PCBs. As devices become interconnected, the need for efficient data transmission and enhanced signal integrity is paramount. Rigid flex PCBs are well-suited for these applications due to their capacity to host multiple components on a single footprint, reducing the number of interconnects and potential failure points. Additionally, the ability to customize the layout of rigid flex PCBs accommodates the design requirements for complex IoT applications, facilitating faster prototyping and production cycles. This adaptability not only enhances performance but also supports innovative designs that can meet the evolving demands of smart technology.
| Application Area | Key Benefits | Future Trends |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | Compact design, improved durability | Integration of IoT features |
| Medical Devices | Reliability, miniaturization | Advanced sensing technologies |
| Aerospace and Defense | Lightweight, high performance | More robust materials |
| Automotive | Enhanced safety features | Electric vehicle integrations |
| Industrial Automation | Efficiency and cost-effectiveness | Smart factory implementations |