In the realm of electronics design, the integration of multi circuit boards has become increasingly vital for enhancing project efficiency and performance. As systems become more complex, the need for streamlined communication and reduced footprint has made multi circuit boards a preferred choice among engineers and designers. According to Dr. Emily Tran, a leading expert in PCB technology, “The effective use of multi circuit boards not only optimizes space but also elevates the reliability and functionality of electronic systems.”
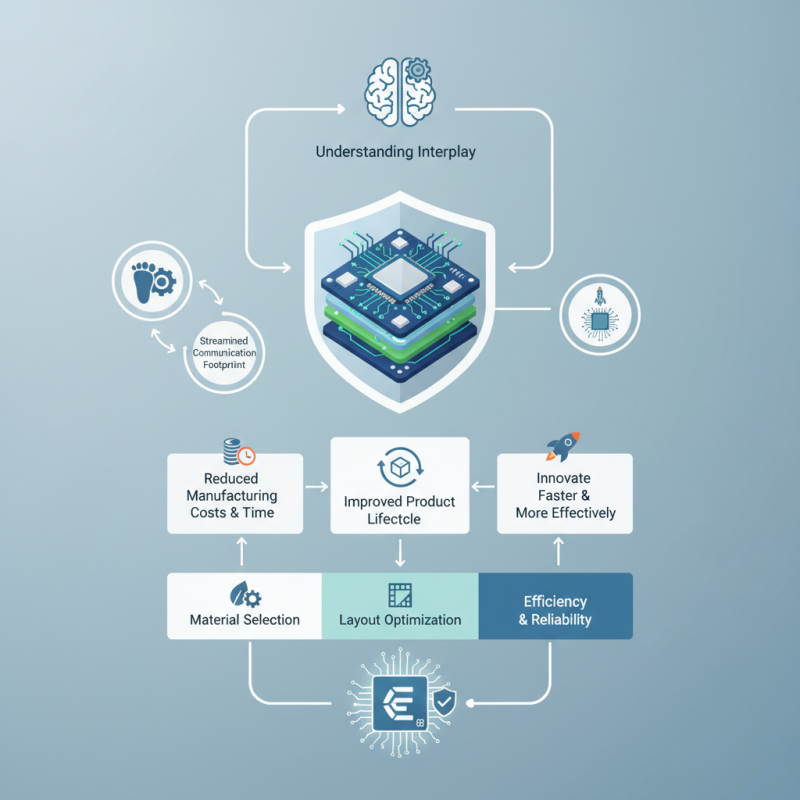
In designing these sophisticated assemblies, understanding the interplay between different circuit functionalities plays a paramount role. Multi circuit boards facilitate various operations across a single platform, which can greatly reduce manufacturing costs and time while improving the overall product lifecycle. By mastering the principles of multi circuit board design, engineers can innovate faster and more effectively, paving the way for advanced electronic applications that are essential in today’s tech-driven world.
This article explores key strategies for designing multi circuit boards that meet the diverse demands of modern electronics projects. From material selection to layout optimization, we will delve into practical tips that can significantly enhance project outcomes while maintaining a high standard of efficiency and reliability.
Designing multi circuit boards (MCBs) requires a solid understanding of their fundamental components and layout techniques. One of the primary aspects of MCB design is effectively managing the complexity that comes with multiple circuits on a single board. According to reports from the electronics industry, 60% of design issues arise from incorrect component placement and insufficient routing strategies. Efficient MCB design not only improves the manufacturability of electronic devices but also enhances performance and reduces costs in production.
When creating an effective MCB layout, it's crucial to consider factors such as thermal management and signal integrity. Modern designs often utilize simulation tools to predict behaviors and interactions between various circuits before the physical board is manufactured. This approach allows designers to minimize potential issues and reduce rework by up to 30%, as supported by analysis from design automation reports.
Tips for Efficient Multi Circuit Board Design:
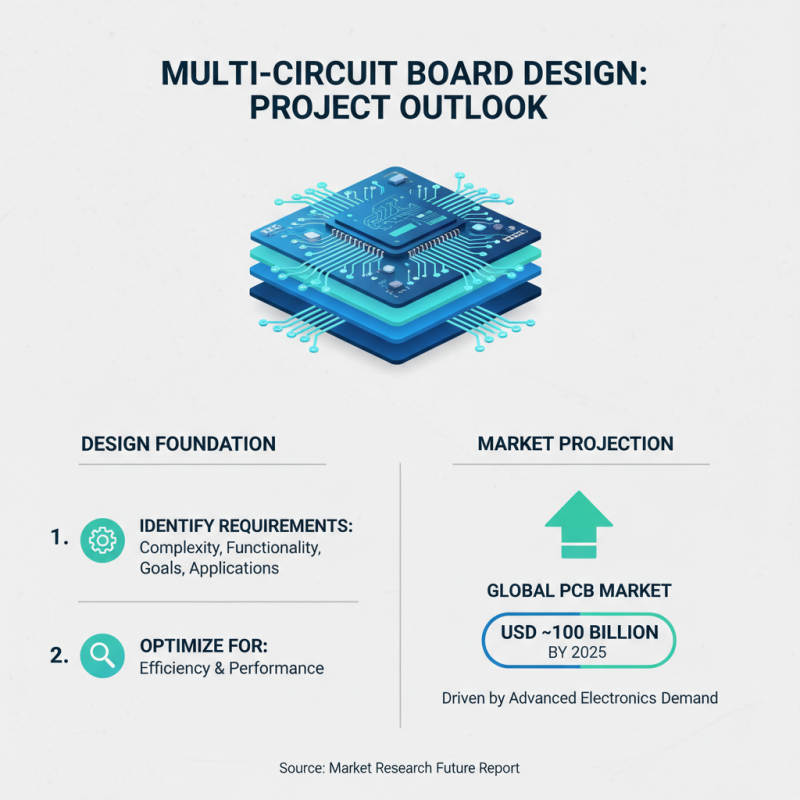
When embarking on the design of multi circuit boards for electronics projects, identifying project requirements and specifications is paramount. Each project varies in complexity and functionality, influenced by specific goals and target applications. According to a report by Market Research Future, the global printed circuit board (PCB) market is projected to reach approximately USD 100 billion by 2025, driven by the growing demand for advanced electronic devices and systems. This underscores the importance of thoroughly understanding project requirements to achieve optimal efficiency and performance in circuitry design.
The initial step in identifying specifications involves a clear understanding of the end application. For instance, power requirements, signal integrity, and thermal management are crucial parameters that directly impact board design. Data from IPC-2221, the standard for generic PCB design, highlights that neglecting these aspects can lead to failures or inefficiencies, particularly in high-frequency applications where impedance control becomes critical. Furthermore, guidelines such as designing for manufacturability (DFM) can help reduce production costs and improve yield rates by ensuring that designs align with fabrication capabilities. Defining these requirements meticulously not only enhances performance but also aligns with industry standards, ensuring reliability and sustainability in the design of multi circuit boards.
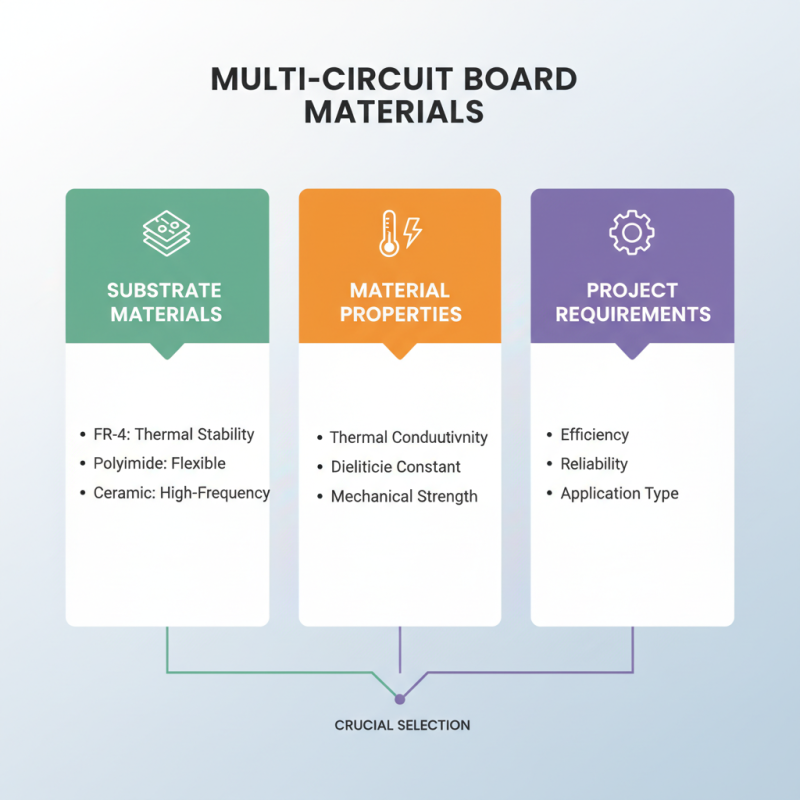
When designing multi circuit boards for electronics projects, selecting appropriate materials and components is crucial for ensuring efficiency and reliability. First, the choice of substrate material significantly impacts the performance of the circuit board. Common materials include FR-4, which offers excellent thermal stability and electrical insulation, and other advanced options such as polyimide for flexible designs or ceramic for high-frequency applications. The thermal conductivity, dielectric constant, and mechanical properties of the substrate must be evaluated to match the specific requirements of the project.
In addition to substrates, selecting components such as resistors, capacitors, and ICs is vital for the overall functionality of the circuit. Components should be chosen based on their specifications—such as voltage ratings, tolerance levels, and temperature coefficients—ensuring that they align with the intended electrical performance. Additionally, considering factors like footprint compatibility and power dissipation will aid in creating a compact and efficient design. Ultimately, thorough material and component selection not only enhances the circuit's performance but also contributes to its longevity and reliability in various applications.
Designing multi circuit boards requires strategic planning to optimize both space and efficiency. One effective technique is to utilize a layered design approach, which allows for denser packing of components. By stacking multiple circuit layers, the design can minimize the area required on each board while maintaining accessibility to critical connections. This method not only frees up space but also can enhance signal integrity by reducing the distance between related components.
Tips for optimizing your design include implementing standard component sizes to facilitate layout. This can reduce complexity and allow for quicker iterations in prototyping. Additionally, consider integrating ground and power planes within your design. These planes can significantly reduce electromagnetic interference and improve the overall performance of the circuit, leading to a more reliable final product.
Another technique involves careful routing of traces to minimize their lengths and avoid unnecessary bends. Keeping traces short can reduce resistance and improve signal timing. Consider using vias strategically to transition between layers efficiently. By employing these design techniques, you can achieve a well-optimized multi circuit board that meets the demands of modern electronics projects effectively.
When working with multi circuit boards, testing and troubleshooting become critical steps in ensuring the efficiency and reliability of your electronics projects. The complexity of multiple circuit boards can lead to various issues, including intermittent connections, signal interference, or incorrect voltage levels. A systematic approach to testing can help identify and resolve these challenges.
One effective method is to utilize a multimeter to check continuity throughout the circuit. This step ensures that all connections are secure and functioning properly. Additionally, employing an oscilloscope can help visualize the signal integrity and timing issues that may arise between interconnected boards. Regularly monitoring power levels and inspecting solder joints can also prevent potential failures down the line.
Tips:
- Always label your circuits during the design phase to simplify troubleshooting later on.
- Use modular components whenever possible to isolate and test specific sections of your circuit without affecting the entire system.
- Conduct tests in a controlled environment to reduce variables that could impact your measurements.